Amplifying Analog Voltages with the LM358
05.03.2025
Elektronik | Funk | Software
Der Technik-Blog
The application is an important part of LoRaWAN (TTN/TTS) and is primarily responsible for the data exchange between the end device and the Internet. There are also LoRaWAN servers that do not have an application, such as the Helium network. This article is about the different tasks of the application in LoRaWAN networks like The Tings Stack (TTN) or Chirpstack.
LoRaWAN & TTN with ESP32 Board
MikroTIK LR8 Gateway with TTN V3 (German)
ProjectLoRaWAN GPS-Tracker with TTGO T-Beam
LoRa Helium Network (German)
Before you can even register a device (node) in the respective LoRaWAN network, you must first create an application. You can think of the application as a folder in Windows Explorer containing individual files. Each file in this folder would represent an end device. An application can also contain more than one end device.In practice, all identical sensors are usually assigned to the same application.
In addition to an optional name and a description, each application has an Application-ID. The Application-ID is a unique ID and consists of up to 36 characters. Lowercase letters, numbers and hyphens can be used as characters. The application ID can only be registered once in the LoRaWAN network.
LoRaWAN tries to save every unnecessary byte of data during transmission. This is achieved by combining individual measured values in a chain of hexadecimal numbers. What has been encoded in the end device must be decoded again after data transmission. This task is performed by the payload decoder in the application. The decoder then passes the data on to the integration in a JSON format. If several identical devices are operated in one application, one decoder is usually sufficient. Starting with TTN V3, each individual node can also be assigned its own encoder/decoder. The encoder works in reverse to the decoder and converts individual parameters into the hexadecimal payload, which is then sent from the LoRaWAN network to the node. More information about the payload can be found in the LoRaWAN Payload article (German only).
The integration is the interface between the LoRaWAN network with the end devices and the Internet. It is a collection of different protocols and services that process and store the received sensor data. The user has to take care of the processing and storage of the data himself, which is why at least one integration has to be set up. MQTT interfaces or webhooks are popular (example: GPS Tracker HTTP webhook (German only)). With a custom webhook, the received data can be forwarded to a custom web server using HTTP/HTTPS POST. There are also numerous integrations to various cloud services such as AWS or Microsoft Azure.
Via collaborators several users can get access to the respective application. Each user account has a unique ID at TTN/TTS, which is stored in the application. Each user can be assigned individual rights to the application. If a new user is registered, the application automatically appears in his account with the permissible rights.

The LoRaWAN FRM payload includes numerous headers, the encrypted payload, and an integrity code. This article explains the structure of an uplink message
read more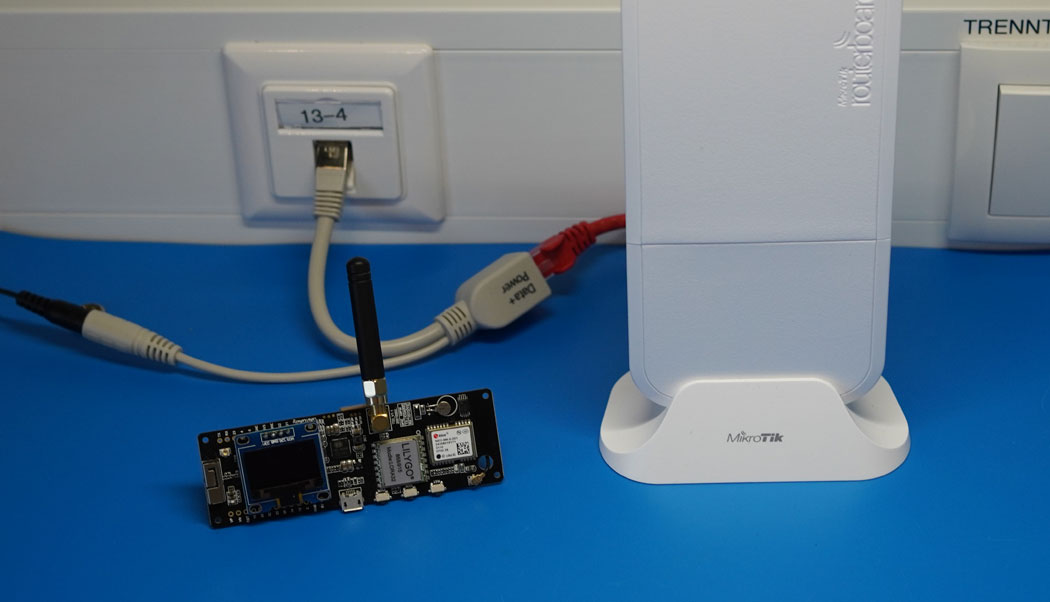
The UDP packet forwarder developed by Semtech handles the data transmission of the received packets from the LoRaWAN gateway to the network server
read moreAEQ-WEB © 2015-2026 All Right Reserved